
As such, they are often seen as disposable and less critical than permanent accounts, which can remain open for extended periods. Temporary accounts are called nominal accounts because they don’t carry a balance from one period to another. Instead, all balances in these accounts must be zeroed out at the end of each reporting period so that financial statements accurately reflect only current activity. Since permanent and temporary accounts come differently, understanding how to classify them properly helps businesses implement strong internal controls over their finances.
Financial Statements
- My site utilizes a unique process that leverages AI and human subject matter expertise to create the best content possible.
- When you report your end-of-year income, you’ll calculate the profits you made by selling that inventory.
- It shows you how much you sold, what it cost, and how much you really earned without having to track every single transaction all year long.
- Download our FREE whitepaper, How to Set up Your Accounting Books for the First Time, for the scoop.
- Lastly, since most organizations use accrual-based accounting systems, they must transfer any unused amounts held in a temporary account into another account once the period has expired.
COGS only includes the direct costs of production, while operating expenses encompass other expenses incurred to operate the business. There are advantages and disadvantages to both the perpetual and periodic inventory systems. The main difference is that assets are valued at net realizable value and can be increased or decreased as values change.
- For the year ended 31 December 2022, CCC recorded sales of $120,000 in the revenue account, $60,000 in the cost of goods sold account and $20,000 in the administrative expense account.
- To correct this situation, all 3 temporary accounts need to be closed on 31 December 2022 with their balances transferred to a permanent account.
- The main difference is that assets are valued at net realizable value and can be increased or decreased as values change.
- These costs include transportation fees for shipping raw materials or goods from suppliers to a company’s warehouse or production facility.
- Understanding the different types of accounts makes it easier for auditors to assess the financial status of a business accurately.
- While this might sound like a small difference, it changes how you interpret the balance for each account type.
Example 5: Adjusting for Depreciation Expense

Understanding the way costs flow these accounts can help you implement a periodic accounting system in your company. Knowing which accounts are permanent or temporary allows for more accurate and timely financial reporting. Permanent accounts capture the long-term effects of business transactions, such as cash inflows from customers, inventory purchases, loans taken out by the company, etc. In contrast, temporary accounts provide a snapshot of income and expenses over a specific period. This process resets these accounts to zero in preparation for the next accounting period and updates the retained earnings account with the net income or loss for the year. Accounts are closed at year-end to transfer the balances of temporary accounts, such as revenues, expenses, and dividends, to retained earnings or the owner’s capital account.
Optimized cash flow
A company may not have correct inventory stock and could make financial decisions based on incorrect data. Square accepts many payment types and updates accounting records is cost of goods sold a temporary account every time a sale occurs through a cloud-based application. Square, Inc. has expanded their product offerings to include Square for Retail POS. This enhanced product allows businesses to connect sales and inventory costs immediately.
Dividends Accounts
To do this, we will do the opposite of the balance in the adjusted trial balance in a journal entry and use Income Summary to balance the entry. Keep in mind, this isn’t your final taxable income—you’ll still need to subtract operating expenses (like rent, utilities, marketing, etc.) from your gross profit of $540. The periodic inventory system helps you keep things simple while still giving you the information you need to see how your business is doing. It shows you how much you how is sales tax calculated sold, what it cost, and how much you really earned without having to track every single transaction all year long. We will help you understand how temporary accounts work, why we must close them at the end of the year, and where the money in them goes.
- Periodic inventory accounting rules calculate the balance of the cost of goods sold account once a month.
- That happens when you move the temporary account balances at the end of the year into a permanent account.
- Knowing this information can help businesses make more informed decisions about allocating resources.
- This isn’t just sales; it can also include interest earned, rental income, or any other sources of revenue.
- At the end of the period, these accounts are closed out, with their balances being transferred to permanent accounts.
- Freight costs not directly tied to production or acquisition are excluded from COGS.
- This process helps ensure all financial information recorded in an organization’s books is correct and up-to-date.
Revenue Accounts
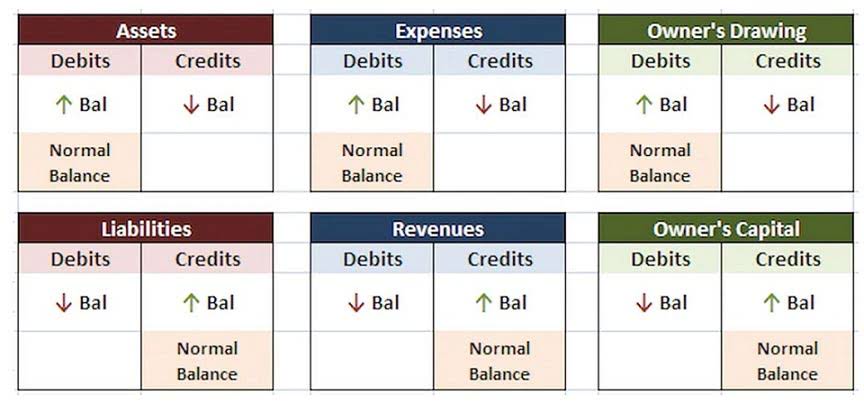
Fixed and long-term accounts are typically used for investments, savings, and other financial instruments to keep money safe over time. Generally speaking, these types of accounts will have higher interest rates than regular checking or savings accounts since they represent a longer commitment from the customer. Sales Discounts, Sales Returns and Allowances, and Cost of Goods Sold will close with the temporary debit balance accounts to Income Summary.
LIFO Method
At the end of the fiscal year, closing entries are used to shift the entire balance in every temporary account into retained earnings, which is a permanent account. The net amount of the balances shifted constitutes the gain or loss that the company earned during the period. After the closing entries have been completed, the ending balances in the temporary accounts are zero, and are Bookkeeping for Etsy Sellers now ready to accumulate transactions for the next fiscal year. Non-temporary accounts include savings, checking, investment, retirement, and credit card accounts.
- And before the start of the new year, the temporary accounts must return to a zero balance.
- The cost of goods sold is calculated by subtracting the opening inventory from the sum of the purchases and the closing inventory.
- For example, say you have $100 of inventory on hand at the beginning of the period and you purchase $500 of additional inventory throughout the month.
- The net amount of the balances shifted constitutes the gain or loss that the company earned during the period.
- The key difference helps maintain clear financial reporting across accounting periods.
- Although a periodic physical count of inventory is still required, a perpetual inventory system may reduce the number of times physical counts are needed.

Understanding the difference between temporary and permanent accounts can be valuable, especially for those in accounting. There are accounts considered temporary, meaning they only last for a specific time, and there are also permanent accounts. The biggest disadvantages of using the perpetual inventory systems arise from the resource constraints for cost and time. This may prohibit smaller or less established companies from investing in the required technologies. The time commitment to train and retrain staff to update inventory is considerable. In addition, since there are fewer physical counts of inventory, the figures recorded in the system may be drastically different from inventory levels in the actual warehouse.

Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) Explained With Methods to Calculate It
Welcome to AccountingJournalEntries.com, your ultimate resource for mastering journal entries in accounting. Enhance your accounting skills and knowledge with our comprehensive resources tailored for professionals and students alike. An important concept in accounting standards is the separation of financial periods. This means that recording a transaction in the period in which they occurred is paramount.